Understanding many-body physics in one dimension from the Lieb–Liniger model
Understanding many-body physics in one dimension from the Lieb–Liniger model |
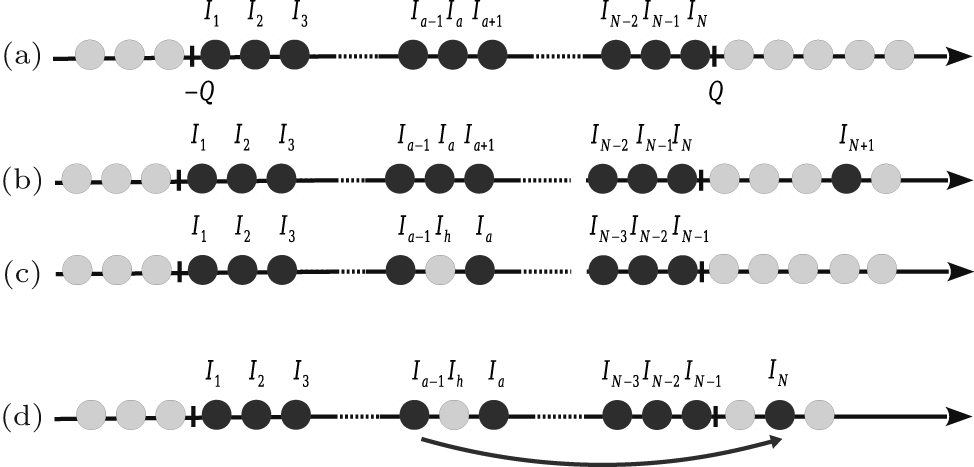
| Schematic diagrams of the ground state and elementary excitations. (a) Quantum numbers for the ground state. The quantum numbers for the ground state are symmetric around the the origin. The largest quasimomentum denotes the “Fermi points” ± Q . (b) Configuration of adding a particle near the right Fermi point with the quantum number I N +1, so that the total number of particles is N + 1. (c) A hole excitation. The hole at I h is created so that the total number of particles is N − 1. In panels (b) and (c), the parities of their quantum numbers are changed from half-odd (or integers) to integer (or half-odds) due to the changes of particle numbers. (d) A single particle–hole excitation. A particle at the position I h is excited out of the pseudo Fermi sea. In this case, the total number of particles is still N , and the parity of quantum numbers dose not change. |
 |