Absorption of ultrashort intense lasers in laser–solid interactions
Absorption of ultrashort intense lasers in laser–solid interactions |
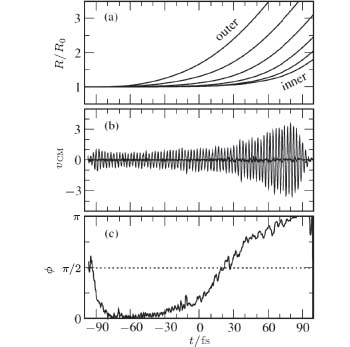
| Fig. 4. Dynamics of Xe 923 cluster in a strong laser pulse #cod#x03BB; #cod#x003D;780 nm, I #cod#x003D; 9 #cod#x00D7; 10 14 Wcm 2 , rise and fall time 20 fs, plateau for t #cod#x003D; #cod#x2212;80,#cod#x2026;,#cod#x002B;80 fs. All quantities are shown as a function of time t : a radii R of all cluster shells in units of their initial radii R 0 , b center-of-mass velocity v CM of the electronic cloud inside the cluster volume, c phase shift #cod#x03A6; t of the collective oscillation in the laser direction with respect to the driving laser. Note that the oscillations are spatially along the linear polarization of the laser, whereas the electron velocity perpendicular to the laser polarization is very small. [ 63 ] |
 |